tunnel
Tunnel acts as the bridge between edge and cloud. It consists of tunnel-cloud and tunnel-edge, which is responsible for maintaining persistent cloud-to-edge network connection. It allows edge nodes with no public IP assigned to be managed by Kubernetes on the cloud to obtain unified and centralized operation and maintenance.
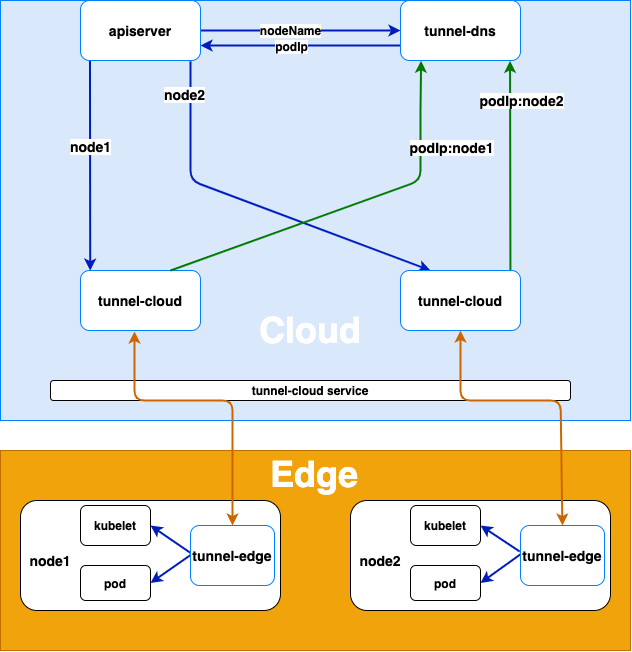
Architecture Diagram
Implementation
Node Registration
- The tunnel-edge on the edge node actively connects to tunnel-cloud service, and tunnel-cloud service transfers the request to the tunnel-cloud pod according to the load balancing policy.
- After tunnel-edge establishes a gRPC connection with tunnel-cloud, tunnel-cloud will write the mapping of its podIp and nodeName of the node where tunnel-edge is located into DNS。If the gRPC connection is disconnected, tunnel-cloud will delete the podIp and node name mapping.
Cloud Request Forwarding
- When apiserver or other cloud applications access the kubelet or other applications on the edge node, the tunnel-dns uses DNS hijacking (resolving the node name in the host to the podIp of tunnel-cloud) to forward the request to the pod of the tunnel-cloud.
- The tunnel-cloud forwards the request information to the gRPC connection established with the tunnel-edge according to the node name.
- The tunnel-edge requests the application on the edge node according to the received request information.
Configuration File
The tunnel component includes tunnel-cloud and tunnel-edge. The tunnel-edge running on the edge node establishes a gRPC long-lived with the tunnel-cloud running on the cloud, which is used to forward the tunnel from the cloud to the edge node.
Tunnel-cloud
The tunnel-cloud contains three modules of stream, TCP and HTTPS. The stream module includes gRPC server and dns components. The gRPC server is used to receive gRPC long-lived requests from tunnel-edge, and the dns component is used to update the node name and IP mapping in the tunnel-cloud memory to the coredns hosts plug-in configmap.
Tunnel-cloud Configuration
tunnel-cloud-conf.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: tunnel-cloud-conf
namespace: edge-system
data:
tunnel_cloud.toml: |
[mode]
[mode.cloud]
[mode.cloud.stream] # stream module
[mode.cloud.stream.server] # gRPC server component
grpcport = 9000 # listening port of gRPC server
logport = 8000 # The listening port of the http server for log and health check,use (curl -X PUT http://podip:logport/debug/flags/v -d "8") to set the log level
channelzaddr = "0.0.0.0:6000" # The listening address of the gRPC [channlez](https://grpc.io/blog/a-short-introduction-to-channelz/)server, used to obtain the debugging information of gRPC
key = "../../conf/certs/cloud.key" # The server-side private key of gRPC server
cert = "../../conf/certs/cloud.crt" # Server-side certificate of gRPC server
tokenfile = "../../conf/token" # The token list file (nodename: random string) is used to verify the token sent by the edge node tunneledge. If the verification fails according to the node name, the token corresponding to the default will be used to verify
[mode.cloud.stream.dns] # DNS component
configmap= "proxy-nodes" # configmap of the configuration file of the coredns hosts plugin
hosts = "/etc/superedge/proxy/nodes/hosts" # The path of the configmap of the configuration file of the coredns hosts plugin in the mount file of the tunnel-cloud pod
service = "proxy-cloud-public" # tunnel-cloud service name
debug = true # DNS component switch, debug=true dns component is closed, the node name mapping in the tunnel-cloud memory will not be saved to the configmap of the coredns hosts plug-in configuration file, the default value is false
[mode.cloud.tcp] # TCP module
"0.0.0.0:6443" = "127.0.0.1:6443" # The parameter format is "0.0.0.0:cloudPort": "EdgeServerIp:EdgeServerPort", cloudPort is the server listening port ofthe tunnel-cloud TCP module, EdgeServerIp and EdgeServerPort are the IP and port of the edge node server forwarded by the proxy
[mode.cloud.https] # HTTPS module
cert ="../../conf/certs/kubelet.crt" # HTTPS module server certificate
key = "../../conf/certs/kubelet.key" # HTTPS module server private key
[mode.cloud.https.addr] # The parameter format is "httpsServerPort": "EdgeHttpsServerIp: EdgeHttpsServerPort", httpsServerPort is the listening port of the HTTPS module server, EdgeHttpsServerIp:EdgeHttpsServerPort is the proxy forwarding the IP and port of the edge node HTTPS server, The server of the HTTPS module skips verifying the client certificate, so you can use (curl -k https://podip:httpsServerPort) to access the port monitored by the HTTPS module. The data type of the addr parameter is map, which can support monitoring multiple ports.
"10250" = "101.206.162.213:10250"
Tunnel-edge
The tunnel-edge also contains three modules of stream, TCP and HTTPS. The stream module includes the gRPC client component, which is used to send gRPC long-lived requests to the tunnel-cloud.
Tunnel-edge Configuration
tunnel-edge-conf.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: tunnel-edge-conf
namespace: edge-system
data:
tunnel_edge.toml: |
[mode]
[mode.edge]
[mode.edge.stream] # stream module
[mode.edge.stream.client] # gRPC client component
token = "6ff2a1ea0f1611eb9896362096106d9d" # Authentication token for access to tunnel-cloud
cert = "../../conf/certs/ca.crt" # The ca certificate of the server-side certificate of the gRPC server of tunnel-cloud is used to verify the server-side certificate
dns = "localhost" # The IP or domain name signed by the gRPC server certificate of tunnel-cloud
servername = "localhost:9000" # The IP and port of gRPC server of tunnel-cloud
logport = 7000 # The listening port of the http server for log and health check,use (curl -X PUT http://podip:logport/debug/flags/v -d "8") to set the log level
channelzaddr = "0.0.0.0:5000" # The listening address of the gRPC channlez server, used to obtain the debugging information of gRPC
[mode.edge.https]
cert= "../../conf/certs/kubelet-client.crt" # The client certificate of the HTTPS server forwarded by tunnel-cloud proxy
key= "../../conf/certs/kubelet-client.key" # The private key of the client side of the HTTPS server forwarded by the tunnel-cloud proxy
Tunnel Forwarding Mode
Tunnel proxy supports either TCP or HTTPS request forwarding.
TCP Forwarding
The TCP module will forward the TCP request to the first edge node connected to the cloud. When there is only one tunnel-edge connected to the tunnel-cloud, The request will be forwarded to the node where the tunnel-edge is located
Tunnel-cloud Configuration
tunnel-cloud-conf.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: tunnel-cloud-conf
namespace: edge-system
data:
tunnel_cloud.toml: |
[mode]
[mode.cloud]
[mode.cloud.stream]
[mode.cloud.stream.server]
grpcport = 9000
key = "/etc/superedge/tunnel/certs/tunnel-cloud-server.key"
cert = "/etc/superedge/tunnel/certs/tunnel-cloud-server.crt"
tokenfile = "/etc/superedge/tunnel/token/token"
logport = 51000
[mode.cloud.stream.dns]
debug = true
[mode.cloud.tcp]
"0.0.0.0:6443" = "127.0.0.1:6443"
[mode.cloud.https]
The gRPC server of the tunnel-cloud listens on port 9000 and waits for the tunnel-edge to establish a gRPC long-lived. The 6443 request to access the tunnel-cloud will be forwarded to the server with the access address 127.0.0.1:6443 of the edge node.
tunnel-cloud.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: tunnel-cloud-conf
namespace: edge-system
data:
mode.toml: |
{{tunnel-cloud-tcp.toml}}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: tunnel-cloud-token
namespace: edge-system
data:
token: |
default:{{.TunnelCloudEdgeToken}}
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
tunnel-cloud-server.crt: '{{tunnel-cloud-server.crt}}'
tunnel-cloud-server.key: '{{tunnel-cloud-server.key}}'
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: tunnel-cloud-cert
namespace: edge-system
type: Opaque
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: tunnel-cloud
namespace: edge-system
spec:
ports:
- name: proxycloud
port: 9000
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9000
selector:
app: tunnel-cloud
type: NodePort
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: tunnel-cloud
name: tunnel-cloud
namespace: edge-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: tunnel-cloud
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: tunnel-cloud
spec:
serviceAccount: tunnel-cloud
serviceAccountName: tunnel-cloud
containers:
- name: tunnel-cloud
image: superedge/tunnel:v0.2.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /cloud/healthz
port: 51010
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 60
timeoutSeconds: 3
successThreshold: 1
failureThreshold: 1
command:
- /usr/local/bin/tunnel
args:
- --m=cloud
- --c=/etc/superedge/tunnel/conf/mode.toml
- --log-dir=/var/log/tunnel
- --alsologtostderr
volumeMounts:
- name: token
mountPath: /etc/superedge/tunnel/token
- name: certs
mountPath: /etc/superedge/tunnel/certs
- name: conf
mountPath: /etc/superedge/tunnel/conf
ports:
- containerPort: 9000
name: tunnel
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 6443
name: apiserver
protocol: TCP
resources:
limits:
cpu: 50m
memory: 100Mi
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 20Mi
volumes:
- name: token
configMap:
name: tunnel-cloud-token
- name: certs
secret:
secretName: tunnel-cloud-cert
- name: conf
configMap:
name: tunnel-cloud-conf
nodeSelector:
node-role.kubernetes.io/master: ""
tolerations:
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
The TunnelCloudEdgeToken in the configmap of tunnel-cloud-token is a random string used to verify the tunnel-edge; The server-side certificate and private key of gRPC server corresponding to the secret of tunnel-cloud-cert.
Tunnel-edge Configuration
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: tunnel-edge-conf
namespace: edge-system
data:
tunnel_edge.toml: |
[mode]
[mode.edge]
[mode.edge.stream]
[mode.edge.stream.client]
token = "{{.TunnelCloudEdgeToken}}"
cert = "/etc/superedge/tunnel/certs/tunnel-ca.crt"
dns = "{{ServerName}}"
servername = "{{.MasterIP}}:9000"
logport = 51000
The tunnel-edge uses MasterIP:9000 to access the tunnel-cloud, uses TunnelCloudEdgeToken as the verification token,and sends it to the cloud for verification. The token is the TunnelCloudEdgeToken in the configmap of the tunnel-cloud-token of the deployment of the tunnel-cloud; DNS is the domain name or IP signed by the gRPC server certificate of the tunnel-cloud; MasterIP is the IP of the node where the tunnel-cloud is located, and 9000 is the tunnel-cloud service NodePort.
tunnel-edge.yaml
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: tunnel-edge
rules:
- apiGroups: [ "" ]
resources: [ "configmaps" ]
verbs: [ "get" ]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: tunnel-edge
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: tunnel-edge
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: tunnel-edge
namespace: edge-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: tunnel-edge
namespace: edge-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: tunnel-edge-conf
namespace: edge-system
data:
mode.toml: |
{{tunnel-edge-conf}}
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
tunnel-ca.crt: '{{.tunnel-ca.crt}}'
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: tunnel-edge-cert
namespace: edge-system
type: Opaque
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: tunnel-edge
namespace: edge-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: tunnel-edge
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: tunnel-edge
spec:
hostNetwork: true
containers:
- name: tunnel-edge
image: superedge/tunnel:v0.2.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /edge/healthz
port: 51010
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 180
timeoutSeconds: 3
successThreshold: 1
failureThreshold: 3
resources:
limits:
cpu: 20m
memory: 20Mi
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 10Mi
command:
- /usr/local/bin/tunnel
env:
- name: NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
args:
- --m=edge
- --c=/etc/superedge/tunnel/conf/tunnel_edge.toml
- --log-dir=/var/log/tunnel
- --alsologtostderr
volumeMounts:
- name: certs
mountPath: /etc/superedge/tunnel/certs
- name: conf
mountPath: /etc/superedge/tunnel/conf
volumes:
- secret:
secretName: tunnel-edge-cert
name: certs
- configMap:
name: tunnel-edge-conf
name: conf
The ca certificate corresponding to the secret of tunnel-edge-cert to verify the gRPC server certificate; tunnel-edge is deployed in the form of deployment, and the number of copies is 1 , Tcp forwarding now only supports forwarding to a single node.
HTTPS Forwarding
To forward cloud requests to edge nodes through tunnel, you need to use the edge node name as the domain name of the HTTPS request host. Domain name resolution can reuse tunnel-coredns ,To use HTTPS forwarding, you need to deploy tunnel-cloud, tunnel-edge and tunnel-coredns three modules .
Tunnel-cloud Configuration
tunnel-cloud-conf.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: tunnel-cloud-conf
namespace: edge-system
data:
tunnel_cloud.toml: |
[mode]
[mode.cloud]
[mode.cloud.stream]
[mode.cloud.stream.server]
grpcport = 9000
logport = 51010
key = "/etc/superedge/tunnel/certs/tunnel-cloud-server.key"
cert = "/etc/superedge/tunnel/certs/tunnel-cloud-server.crt"
tokenfile = "/etc/superedge/tunnel/token/token"
[mode.cloud.stream.dns]
configmap = "tunnel-nodes"
hosts = "/etc/superedge/tunnel/nodes/hosts"
service = "tunnel-cloud"
[mode.cloud.https]
cert = "/etc/superedge/tunnel/certs/apiserver-kubelet-server.crt"
key = "/etc/superedge/tunnel/certs/apiserver-kubelet-server.key"
[mode.cloud.https.addr]
"10250" = "127.0.0.1:10250"
The gRPC server of the tunnel-cloud listens on port 9000 and waits for the tunnel-edge to establish a gRPC long-lived. The request to access tunnel-cloud 10250 will be forwarded to the server with the access address 127.0.0.1:10250 of the edge node.
tunnel-cloud.yaml
Tunnel-edge Configuration
tunnel-edge-conf.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: tunnel-edge-conf
namespace: edge-system
data:
tunnel_edge.toml: |
[mode]
[mode.edge]
[mode.edge.stream]
[mode.edge.stream.client]
token = "{{.TunnelCloudEdgeToken}}"
cert = "/etc/superedge/tunnel/certs/cluster-ca.crt"
dns = "tunnel.cloud.io"
servername = "{{.MasterIP}}:9000"
logport = 51000
[mode.edge.https]
cert = "/etc/superedge/tunnel/certs/apiserver-kubelet-client.crt"
key = "/etc/superedge/tunnel/certs/apiserver-kubelet-client.key"
The certificate and private key of the HTTPS module are the client certificate corresponding to the server-side certificate of the server of the edge node forwarded by the tunnel-cloud. For example, when tunnel-cloud forwards the request from apiserver to kubelet, it is necessary to configure the client certificate and private key corresponding to the kubelet port 10250 server certificate.
tunnel-edge.yaml
Local Debugging
Tunnel supports HTTPS (HTTPS module) and TCP protocol (TCP module). The data of the protocol module is transmitted through gRPC long-lived (stream module ), so it can be divided into modules for local debugging. Local debugging can use go’s testing framework. The configuration file can be generated by calling config_test test method Test_Config (where the constant variable config_path is the path of the generated configuration file relative to the path of the config_test go file, and main_path is the configuration file relative to the test file Path), such as the local debugging of the stream module: config_path = “../../../conf” (The generated configuration file is in the conf folder under the root directory of the project), then main_path="../../../../conf"(the path of stream_test relative to conf), the configuration file is generated to support the configuration of ca.crt and ca.key (when configpath/certs/ca.crt and configpath/certs/ca.key exist, the specified ca is used to issue the certificate).
stream module debugging
start of the stream server
func Test_StreamServer(t *testing.T) {
err := conf.InitConf(util.CLOUD, "../../../../conf/cloud_mode.toml")
if err != nil {
t.Errorf("failed to initialize stream server configuration file err = %v", err)
return
}
model.InitModules(util.CLOUD)
InitStream(util.CLOUD)
model.LoadModules(util.CLOUD)
context.GetContext().RegisterHandler(util.MODULE_DEBUG, util.STREAM, StreamDebugHandler)
model.ShutDown()
}
Load configuration file(conf.InitConf)->Initialize the module(model.InitMoudule)->Initialize the stream module(InitStream)->Load the initialized module->Register a custom handler (StreamDebugHandler)->Shut down the module (model.ShutDown)
StreamDebugHandler is a custom handler for debugging cloud side messaging
start of the stream client
func Test_StreamClient(t *testing.T) {
os.Setenv(util.NODE_NAME_ENV, "node1")
err := conf.InitConf(util.EDGE, "../../../../conf/edge_mode.toml")
if err != nil {
t.Errorf("failed to initialize stream client configuration file err = %v", err)
return
}
model.InitModules(util.EDGE)
InitStream(util.EDGE)
model.LoadModules(util.EDGE)
context.GetContext().RegisterHandler(util.MODULE_DEBUG, util.STREAM, StreamDebugHandler)
go func() {
running := true
for running {
node := context.GetContext().GetNode(os.Getenv(util.NODE_NAME_ENV))
if node != nil {
node.Send2Node(&proto.StreamMsg{
Node: os.Getenv(util.NODE_NAME_ENV),
Category: util.STREAM,
Type: util.MODULE_DEBUG,
Topic: uuid.NewV4().String(),
Data: []byte{'c'},
})
}
time.Sleep(10 * time.Second)
}
}()
model.ShutDown()
}
Set the node name environment variable->Load configuration file (conf.InitConf)->Initialization module (model.InitMoudule)->Initialize the stream module (InitStream)->Load the initialized module->Register a custom handler (StreamDebugHandler)->Shut down the module (model.ShutDown)
The node name is loaded through the environment variable of NODE_NAME
TCP module debugging
TCP server debugging
func Test_TcpServer(t *testing.T) {
err := conf.InitConf(util.CLOUD, "../../../../conf/cloud_mode.toml")
if err != nil {
t.Errorf("failed to initialize stream server configuration file err = %v", err)
return
}
model.InitModules(util.CLOUD)
InitTcp()
stream.InitStream(util.CLOUD)
model.LoadModules(util.CLOUD)
model.ShutDown()
}
Need to initialize the TCP module (InitTcp) and the stream module (stream.InitStream) at the same time
TCP client debugging
func Test_TcpClient(t *testing.T) {
os.Setenv(util.NODE_NAME_ENV, "node1")
err := conf.InitConf(util.EDGE, "../../../../conf/edge_mode.toml")
if err != nil {
t.Errorf("failed to initialize stream client configuration file err = %v", err)
return
}
model.InitModules(util.EDGE)
InitTcp()
stream.InitStream(util.EDGE)
model.LoadModules(util.EDGE)
model.ShutDown()
}
HTTPS module debugging
Similar to TCP module debugging, HTTPS module and stream module need to be loaded at the same time.
Debugging of tunnel main() function
In the main test file of the tunnel tunnel_test, you need to use init() set the parameters, at the same time you need to use TestMain to parse the parameters and call the test method
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear from you! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.